Introduction
This describes the implementation of Continuous Integration on the Talend software platform. The following sections are included:
- Overview of process and the required software
- Set up of the required server over and standard Talend setup
- Installation and configuration of the required software
- Setting up the integration tests
- Running the integration tests
- Promoting artifacts to Talend Cloud
This blog is intended as an introduction and user guide for both the setup of and running of the continuous integration features within Talend, focusing on the use of Jenkins and Maven. It is not meant to be a replacement for the SDLC guide but a compliment to it.
Continuous Integration
Continuous integration is a development practice where members of a team integrate their work frequently, with each integration being verified by an automated build to detect errors as quickly as possible.

Why Continuous Integration?
Let’s dig into what implementing continuous integration to your everyday software development process can bring to the table. Realizing these benefits means reducing risks for each build and clearing the way to get your valuable features out to customers faster.
- Continuous integration tools when properly used it will remove much of this headache by providing you with quick answers to the question “did I break something?” for each commit.
- Metrics generated from automated testing and CI (such as metrics for code coverage, code complexity, and features complete) focus developers on developing functional, quality code, and help develop momentum in a team.
- You can see which changes tend to break builds more often.
- Continuous integration supports connecting the pieces of your software every day.
- If various kinds of useful automated tests are run in your continuous integration pipeline, you’ll be able to know what to fix as soon as a test fails.
- The easier it is to test something, the easier it is to determine its quality.
- Avoids last-minute chaos at release dates, when everyone tries to check in their slightly incompatible versions
Additional third party software’s
To enable Continuous integration for Talend Cloud Platform, the following software is required:
- Install Java
- Install Maven
- Install Jenkins
- Install Nexus
- Install Talend Studio
Let’s start continuous integration for Talend Cloud
- Create an simple talend job in Talend Studio.
- And push it to Git repository.
3. Create a Maven project in Jenkins.
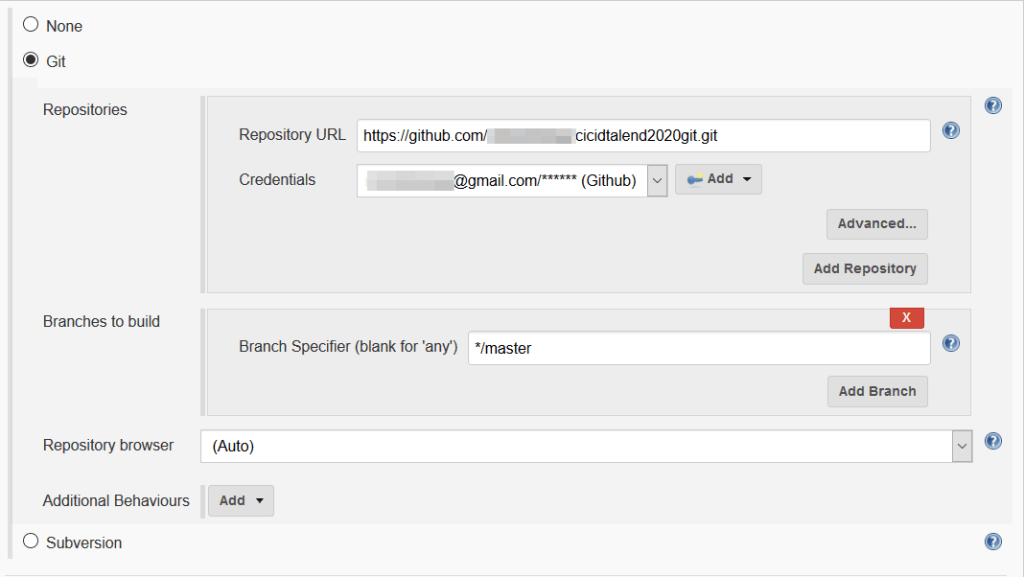
4. Enter git url and its credentials in “Source Code Management”.
5. Check Delete workspace before build starts in “Build Environment”.

6. In “Build” provide Root POM, Goals and options and MAVEN_OPTS.
- Root POM : You need to provide “<workspace location>\<project name>\poms\pom.xml”. It will be generate by talend which consistent of talend project details, version details, jar dependency and there versions, etc..
- Goals and options : You need to provide maven life cycle options to build or deploy code or publish to cloud
- MAVEN_OPTS : You need to provide maven configuration details to build or deploy to cloud.

7. And you should provide custom workspace for jenkins it can able to download git code into target workspace and compile to binary’s.

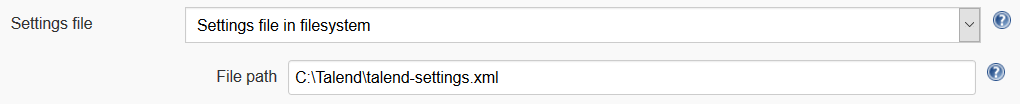
8. And also you should specify custom setting.xml where you need to point .m2 repository to Talend Studio .m2 repository.

9. Hooray!! it done. Sit back wait for its magic to completed.
